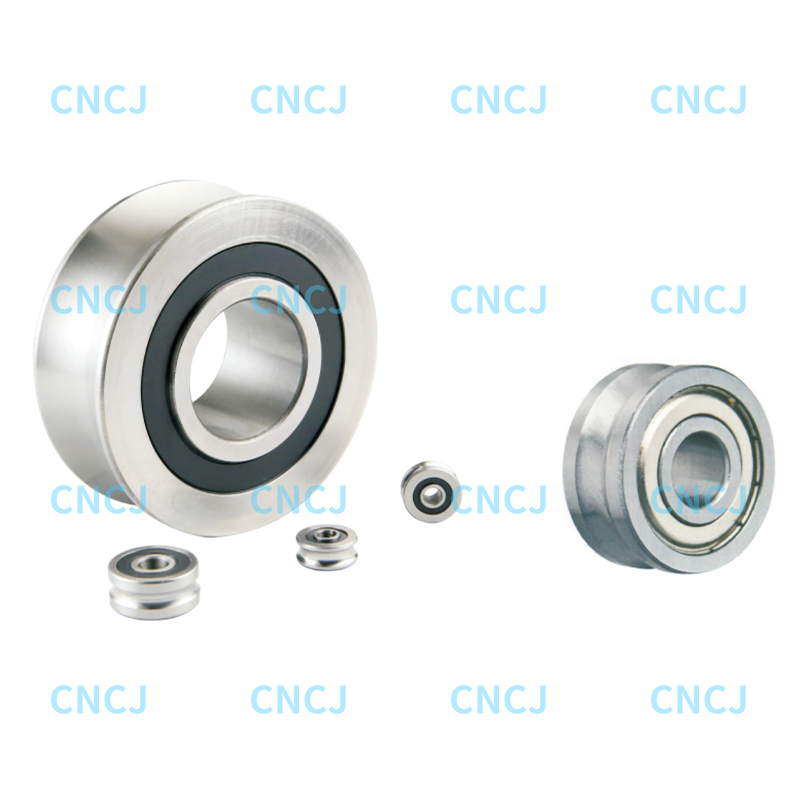
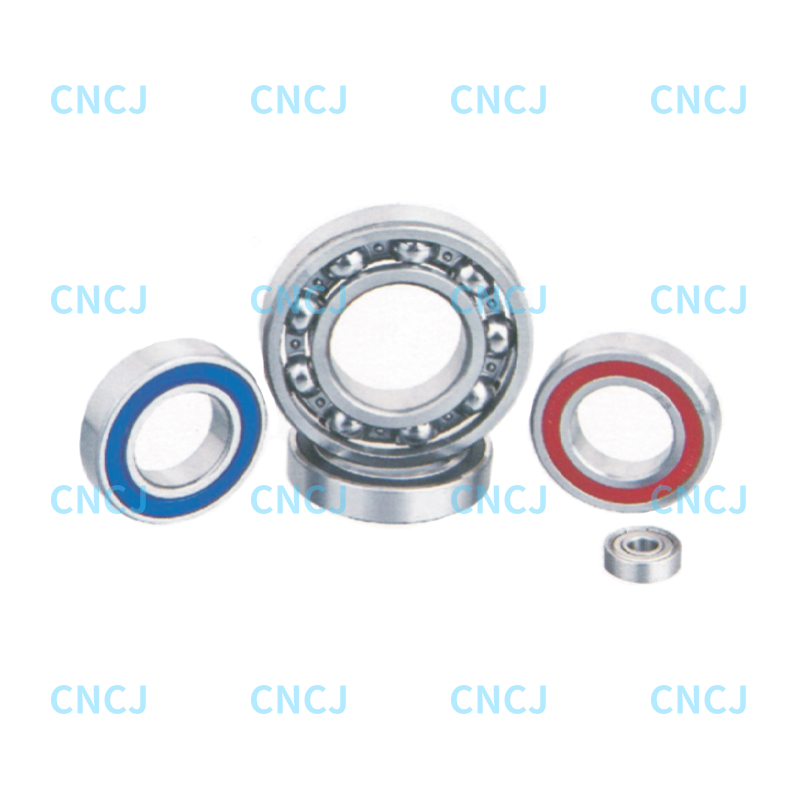
Deep groove ball bearings are designed to withstand both radial and axial loads. Their load-bearing capacity depends on the bearing's structure, size, and conditions of use. Here is a detailed explanation:
1. Radial load
Design features: The rolling elements of deep groove ball bearings are spherical, which allows them to evenly distribute radial loads. The contact lines between the ball and the inner and outer rings are point contacts, which allows the bearings to withstand higher radial loads.
Load capacity: Deep groove ball bearings can operate normally under relatively large radial loads. The deep groove shape of the bearing provides a larger contact surface, increasing the radial load bearing capacity.
2. Axial load
Design features: Deep groove ball bearings can also withstand a certain amount of axial load. Since the contact surfaces between the ball and the inner and outer rings are point contacts, their ability to withstand axial loads is limited.
Load capacity: Deep groove ball bearings can withstand bidirectional axial loads (i.e. loads on both sides of the axial direction), but their load capacity is usually not as good as specially designed axial bearings (such as thrust ball bearings). When designing, it is necessary to ensure that the axial load does not exceed the rated load of the bearing.
3. Combined load
Load combination: In actual applications, deep groove ball bearings usually bear radial loads and axial loads at the same time. Their load capacity is adjusted according to the combination of loads. If the combination of loads exceeds the load capacity of the bearing, it may cause premature failure of the bearing.
Load calculation: When designing and selecting deep groove ball bearings, it is necessary to consider the effects of radial loads and axial loads. Usually, the load calculation formula or manual provided by the bearing manufacturer is used to ensure that the bearing can operate safely in a specific application.
4. Load influencing factors
Bearing size: Larger bearings can generally withstand higher loads. Choosing the appropriate size and specifications is essential to meet the load requirements.
Lubrication: Good lubrication can reduce friction and wear, increase the bearing's load capacity and service life. Regular maintenance and inspection of lubrication status are very important.
Installation accuracy: Correct installation can ensure that the bearing maintains good contact when it is under load and reduce unnecessary stress concentration.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español